window下创建redis出现问题小结
一.准备工作
1.准备一个redis,删除目录下的,dump.rdb文件,并修改他的配置文件:redis.windows.conf
1.修改端口:我设置为 port 7001
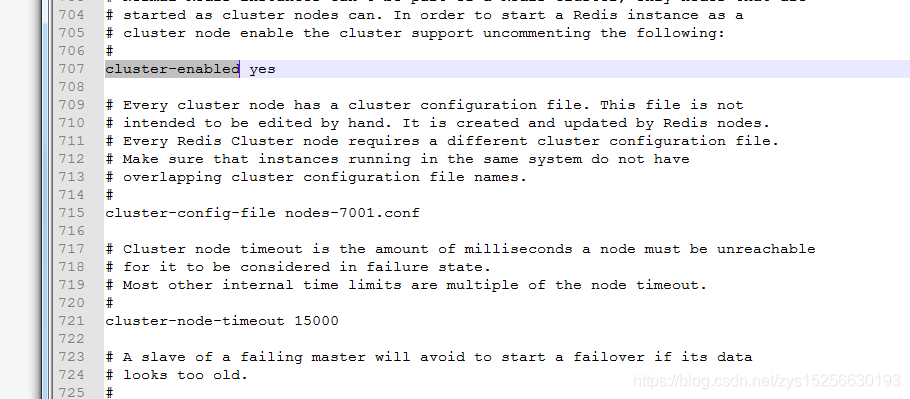
2.放开配置:
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes-7001.conf //名称可自改
cluster-node-timeout 15000

将这个redis复制5份,并修改相应配置,将端口设置为:7001,7002,7003,7004,7005,7006
2.配置Ruby环境、Redis的Ruby驱动redis.gem以及创建Redis集群的工具redis-trib.rb。
(1)下载Redis安装文件:http://download.redis.io/releases/,我们下载zip格式Redis-x64-3.2.1版本。

(2)下载Ruby安装文件:http://dl.bintray.com/oneclick/rubyinstaller/rubyinstaller-2.2.4-x64.exe
(3)下载Ruby环境下Redis的驱动:https://rubygems.org/gems/redis/versions/3.2.2,考虑到兼容性,这里下载的是3.2.2版本。
下载:https://rubygems.org/downloads/redis-3.2.2.gem
(4)下载Redis官方提供的创建Redis集群的ruby脚本文件redis-trib.rb;(我自己下载的,在文章最后,自用)
3.将所有redis文件和redis-trib.rb放在一个redis目录下:
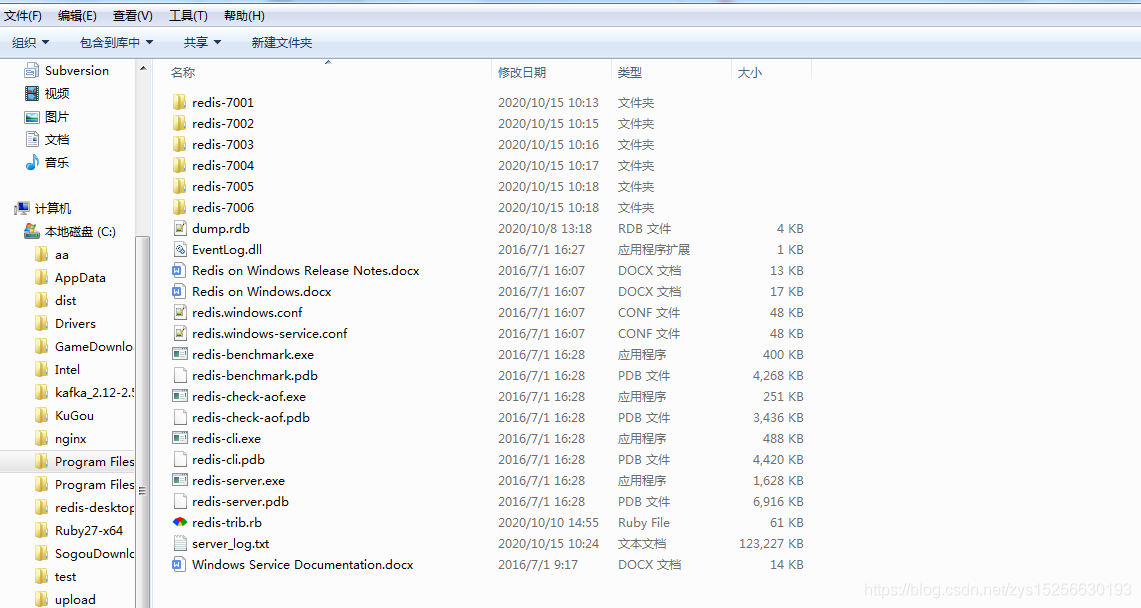
二.启动redis群
1.在redis-trib.rb目录下输入:后面会出现选项,选yes即可;
redis-trib.rb create –replicas 0 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005 127.0.0.1:7006
三.出现问题
1.缺少redis库:
解决方法:gem install redis (安装redis库)

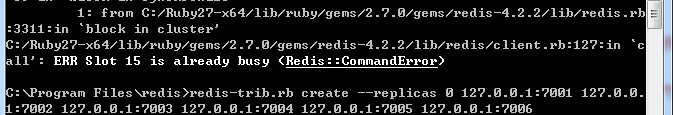
2.插槽15被占用,解决方法:打开每一个服务器,执行flushall、flushdb、cluster reset指令:到每个redis目录下修改:

四.资源
redis-trib.rb:将他复制到文本上并修改文本名称即可:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
# TODO (temporary here, we’ll move this into the Github issues once
# redis-trib initial implementation is completed).
#
# – Make sure that if the rehashing fails in the middle redis-trib will try
# to recover.
# – When redis-trib performs a cluster check, if it detects a slot move in
# progress it should prompt the user to continue the move from where it
# stopped.
# – Gracefully handle Ctrl+C in move_slot to prompt the user if really stop
# while rehashing, and performing the best cleanup possible if the user
# forces the quit.
# – When doing “fix” set a global Fix to true, and prompt the user to
# fix the problem if automatically fixable every time there is something
# to fix. For instance:
# 1) If there is a node that pretend to receive a slot, or to migrate a
# slot, but has no entries in that slot, fix it.
# 2) If there is a node having keys in slots that are not owned by it
# fix this condition moving the entries in the same node.
# 3) Perform more possibly slow tests about the state of the cluster.
# 4) When aborted slot migration is detected, fix it.
require ‘rubygems’
require ‘redis’
ClusterHashSlots = 16384
MigrateDefaultTimeout = 60000
MigrateDefaultPipeline = 10
RebalanceDefaultThreshold = 2
$verbose = false
def xputs(s)
case s[0..2]
when “>>>”
color=”29;1″
when “[ER”
color=”31;1″
when “[WA”
color=”31;1″
when “[OK”
color=”32″
when “[FA”,”***”
color=”33″
else
color=nil
end
color = nil if ENV[‘TERM’] != “xterm”
print “\033[#{color}m” if color
print s
print “\033[0m” if color
print “\n”
end
class ClusterNode
def initialize(addr)
s = addr.split(“:”)
if s.length < 2
puts “Invalid IP or Port (given as #{addr}) – use IP:Port format”
exit 1
end
port = s.pop # removes port from split array
ip = s.join(“:”) # if s.length > 1 here, it’s IPv6, so restore address
@r = nil
@info = {}
@info[:host] = ip
@info[:port] = port
@info[:slots] = {}
@info[:migrating] = {}
@info[:importing] = {}
@info[:replicate] = false
@dirty = false # True if we need to flush slots info into node.
@friends = []
end
def friends
@friends
end
def slots
@info[:slots]
end
def has_flag?(flag)
@info[:flags].index(flag)
end
def to_s
“#{@info[:host]}:#{@info[:port]}”
end
def connect(o={})
return if @r
print “Connecting to node #{self}: ” if $verbose
STDOUT.flush
begin
@r = Redis.new(:host => @info[:host], :port => @info[:port], :timeout => 60)
@r.ping
rescue
xputs “[ERR] Sorry, can’t connect to node #{self}”
exit 1 if o[:abort]
@r = nil
end
xputs “OK” if $verbose
end
def assert_cluster
info = @r.info
if !info[“cluster_enabled”] || info[“cluster_enabled”].to_i == 0
xputs “[ERR] Node #{self} is not configured as a cluster node.”
exit 1
end
end
def assert_empty
if !(@r.cluster(“info”).split(“\r\n”).index(“cluster_known_nodes:1”)) ||
(@r.info[‘db0’])
xputs “[ERR] Node #{self} is not empty. Either the node already knows other nodes (check with CLUSTER NODES) or contains some key in database 0.”
exit 1
end
end
def load_info(o={})
self.connect
nodes = @r.cluster(“nodes”).split(“\n”)
nodes.each{|n|
# name addr flags role ping_sent ping_recv link_status slots
split = n.split
name,addr,flags,master_id,ping_sent,ping_recv,config_epoch,link_status = split[0..6]
slots = split[8..-1]
info = {
:name => name,
:addr => addr,
:flags => flags.split(“,”),
:replicate => master_id,
:ping_sent => ping_sent.to_i,
:ping_recv => ping_recv.to_i,
:link_status => link_status
}
info[:replicate] = false if master_id == “-”
if info[:flags].index(“myself”)
@info = @info.merge(info)
@info[:slots] = {}
slots.each{|s|
if s[0..0] == ‘[‘
if s.index(“->-“) # Migrating
slot,dst = s[1..-1].split(“->-“)
@info[:migrating][slot.to_i] = dst
elsif s.index(“-<-“) # Importing
slot,src = s[1..-1].split(“-<-“)
@info[:importing][slot.to_i] = src
end
elsif s.index(“-“)
start,stop = s.split(“-“)
self.add_slots((start.to_i)..(stop.to_i))
else
self.add_slots((s.to_i)..(s.to_i))
end
} if slots
@dirty = false
@r.cluster(“info”).split(“\n”).each{|e|
k,v=e.split(“:”)
k = k.to_sym
v.chop!
if k != :cluster_state
@info[k] = v.to_i
else
@info[k] = v
end
}
elsif o[:getfriends]
@friends << info
end
}
end
def add_slots(slots)
slots.each{|s|
@info[:slots][s] = :new
}
@dirty = true
end
def set_as_replica(node_id)
@info[:replicate] = node_id
@dirty = true
end
def flush_node_config
return if !@dirty
if @info[:replicate]
begin
@r.cluster(“replicate”,@info[:replicate])
rescue
# If the cluster did not already joined it is possible that
# the slave does not know the master node yet. So on errors
# we return ASAP leaving the dirty flag set, to flush the
# config later.
return
end
else
new = []
@info[:slots].each{|s,val|
if val == :new
new << s
@info[:slots][s] = true
end
}
@r.cluster(“addslots”,*new)
end
@dirty = false
end
def info_string
# We want to display the hash slots assigned to this node
# as ranges, like in: “1-5,8-9,20-25,30”
#
# Note: this could be easily written without side effects,
# we use ‘slots’ just to split the computation into steps.
# First step: we want an increasing array of integers
# for instance: [1,2,3,4,5,8,9,20,21,22,23,24,25,30]
slots = @info[:slots].keys.sort
# As we want to aggregate adjacent slots we convert all the
# slot integers into ranges (with just one element)
# So we have something like [1..1,2..2, … and so forth.
slots.map!{|x| x..x}
# Finally we group ranges with adjacent elements.
slots = slots.reduce([]) {|a,b|
if !a.empty? && b.first == (a[-1].last)+1
a[0..-2] + [(a[-1].first)..(b.last)]
else
a + [b]
end
}
# Now our task is easy, we just convert ranges with just one
# element into a number, and a real range into a start-end format.
# Finally we join the array using the comma as separator.
slots = slots.map{|x|
x.count == 1 ? x.first.to_s : “#{x.first}-#{x.last}”
}.join(“,”)
role = self.has_flag?(“master”) ? “M” : “S”
if self.info[:replicate] and @dirty
is = “S: #{self.info[:name]} #{self.to_s}”
else
is = “#{role}: #{self.info[:name]} #{self.to_s}\n”+
” slots:#{slots} (#{self.slots.length} slots) “+
“#{(self.info[:flags]-[“myself”]).join(“,”)}”
end
if self.info[:replicate]
is += “\n replicates #{info[:replicate]}”
elsif self.has_flag?(“master”) && self.info[:replicas]
is += “\n #{info[:replicas].length} additional replica(s)”
end
is
end
# Return a single string representing nodes and associated slots.
# TODO: remove slaves from config when slaves will be handled
# by Redis Cluster.
def get_config_signature
config = []
@r.cluster(“nodes”).each_line{|l|
s = l.split
slots = s[8..-1].select {|x| x[0..0] != “[“}
next if slots.length == 0
config << s[0]+”:”+(slots.sort.join(“,”))
}
config.sort.join(“|”)
end
def info
@info
end
def is_dirty?
@dirty
end
def r
@r
end
end
class RedisTrib
def initialize
@nodes = []
@fix = false
@errors = []
@timeout = MigrateDefaultTimeout
end
def check_arity(req_args, num_args)
if ((req_args > 0 and num_args != req_args) ||
(req_args < 0 and num_args < req_args.abs))
xputs “[ERR] Wrong number of arguments for specified sub command”
exit 1
end
end
def add_node(node)
@nodes << node
end
def reset_nodes
@nodes = []
end
def cluster_error(msg)
@errors << msg
xputs msg
end
# Return the node with the specified ID or Nil.
def get_node_by_name(name)
@nodes.each{|n|
return n if n.info[:name] == name.downcase
}
return nil
end
# Like get_node_by_name but the specified name can be just the first
# part of the node ID as long as the prefix in unique across the
# cluster.
def get_node_by_abbreviated_name(name)
l = name.length
candidates = []
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.info[:name][0…l] == name.downcase
candidates << n
end
}
return nil if candidates.length != 1
candidates[0]
end
# This function returns the master that has the least number of replicas
# in the cluster. If there are multiple masters with the same smaller
# number of replicas, one at random is returned.
def get_master_with_least_replicas
masters = @nodes.select{|n| n.has_flag? “master”}
sorted = masters.sort{|a,b|
a.info[:replicas].length <=> b.info[:replicas].length
}
sorted[0]
end
def check_cluster(opt={})
xputs “>>> Performing Cluster Check (using node #{@nodes[0]})”
show_nodes if !opt[:quiet]
check_config_consistency
check_open_slots
check_slots_coverage
end
def show_cluster_info
masters = 0
keys = 0
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.has_flag?(“master”)
puts “#{n} (#{n.info[:name][0…8]}…) -> #{n.r.dbsize} keys | #{n.slots.length} slots | “+
“#{n.info[:replicas].length} slaves.”
masters += 1
keys += n.r.dbsize
end
}
xputs “[OK] #{keys} keys in #{masters} masters.”
keys_per_slot = sprintf(“%.2f”,keys/16384.0)
puts “#{keys_per_slot} keys per slot on average.”
end
# Merge slots of every known node. If the resulting slots are equal
# to ClusterHashSlots, then all slots are served.
def covered_slots
slots = {}
@nodes.each{|n|
slots = slots.merge(n.slots)
}
slots
end
def check_slots_coverage
xputs “>>> Check slots coverage…”
slots = covered_slots
if slots.length == ClusterHashSlots
xputs “[OK] All #{ClusterHashSlots} slots covered.”
else
cluster_error \
“[ERR] Not all #{ClusterHashSlots} slots are covered by nodes.”
fix_slots_coverage if @fix
end
end
def check_open_slots
xputs “>>> Check for open slots…”
open_slots = []
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.info[:migrating].size > 0
cluster_error \
“[WARNING] Node #{n} has slots in migrating state (#{n.info[:migrating].keys.join(“,”)}).”
open_slots += n.info[:migrating].keys
end
if n.info[:importing].size > 0
cluster_error \
“[WARNING] Node #{n} has slots in importing state (#{n.info[:importing].keys.join(“,”)}).”
open_slots += n.info[:importing].keys
end
}
open_slots.uniq!
if open_slots.length > 0
xputs “[WARNING] The following slots are open: #{open_slots.join(“,”)}”
end
if @fix
open_slots.each{|slot| fix_open_slot slot}
end
end
def nodes_with_keys_in_slot(slot)
nodes = []
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.has_flag?(“slave”)
nodes << n if n.r.cluster(“getkeysinslot”,slot,1).length > 0
}
nodes
end
def fix_slots_coverage
not_covered = (0…ClusterHashSlots).to_a – covered_slots.keys
xputs “>>> Fixing slots coverage…”
xputs “List of not covered slots: ” + not_covered.join(“,”)
# For every slot, take action depending on the actual condition:
# 1) No node has keys for this slot.
# 2) A single node has keys for this slot.
# 3) Multiple nodes have keys for this slot.
slots = {}
not_covered.each{|slot|
nodes = nodes_with_keys_in_slot(slot)
slots[slot] = nodes
xputs “Slot #{slot} has keys in #{nodes.length} nodes: #{nodes.join(“, “)}”
}
none = slots.select {|k,v| v.length == 0}
single = slots.select {|k,v| v.length == 1}
multi = slots.select {|k,v| v.length > 1}
# Handle case “1”: keys in no node.
if none.length > 0
xputs “The folowing uncovered slots have no keys across the cluster:”
xputs none.keys.join(“,”)
yes_or_die “Fix these slots by covering with a random node?”
none.each{|slot,nodes|
node = @nodes.sample
xputs “>>> Covering slot #{slot} with #{node}”
node.r.cluster(“addslots”,slot)
}
end
# Handle case “2”: keys only in one node.
if single.length > 0
xputs “The folowing uncovered slots have keys in just one node:”
puts single.keys.join(“,”)
yes_or_die “Fix these slots by covering with those nodes?”
single.each{|slot,nodes|
xputs “>>> Covering slot #{slot} with #{nodes[0]}”
nodes[0].r.cluster(“addslots”,slot)
}
end
# Handle case “3”: keys in multiple nodes.
if multi.length > 0
xputs “The folowing uncovered slots have keys in multiple nodes:”
xputs multi.keys.join(“,”)
yes_or_die “Fix these slots by moving keys into a single node?”
multi.each{|slot,nodes|
target = get_node_with_most_keys_in_slot(nodes,slot)
xputs “>>> Covering slot #{slot} moving keys to #{target}”
target.r.cluster(‘addslots’,slot)
target.r.cluster(‘setslot’,slot,’stable’)
nodes.each{|src|
next if src == target
# Set the source node in ‘importing’ state (even if we will
# actually migrate keys away) in order to avoid receiving
# redirections for MIGRATE.
src.r.cluster(‘setslot’,slot,’importing’,target.info[:name])
move_slot(src,target,slot,:dots=>true,:fix=>true,:cold=>true)
src.r.cluster(‘setslot’,slot,’stable’)
}
}
end
end
# Return the owner of the specified slot
def get_slot_owners(slot)
owners = []
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.has_flag?(“slave”)
n.slots.each{|s,_|
owners << n if s == slot
}
}
owners
end
# Return the node, among ‘nodes’ with the greatest number of keys
# in the specified slot.
def get_node_with_most_keys_in_slot(nodes,slot)
best = nil
best_numkeys = 0
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.has_flag?(“slave”)
numkeys = n.r.cluster(“countkeysinslot”,slot)
if numkeys > best_numkeys || best == nil
best = n
best_numkeys = numkeys
end
}
return best
end
# Slot ‘slot’ was found to be in importing or migrating state in one or
# more nodes. This function fixes this condition by migrating keys where
# it seems more sensible.
def fix_open_slot(slot)
puts “>>> Fixing open slot #{slot}”
# Try to obtain the current slot owner, according to the current
# nodes configuration.
owners = get_slot_owners(slot)
owner = owners[0] if owners.length == 1
migrating = []
importing = []
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.has_flag? “slave”
if n.info[:migrating][slot]
migrating << n
elsif n.info[:importing][slot]
importing << n
elsif n.r.cluster(“countkeysinslot”,slot) > 0 && n != owner
xputs “*** Found keys about slot #{slot} in node #{n}!”
importing << n
end
}
puts “Set as migrating in: #{migrating.join(“,”)}”
puts “Set as importing in: #{importing.join(“,”)}”
# If there is no slot owner, set as owner the slot with the biggest
# number of keys, among the set of migrating / importing nodes.
if !owner
xputs “>>> Nobody claims ownership, selecting an owner…”
owner = get_node_with_most_keys_in_slot(@nodes,slot)
# If we still don’t have an owner, we can’t fix it.
if !owner
xputs “[ERR] Can’t select a slot owner. Impossible to fix.”
exit 1
end
# Use ADDSLOTS to assign the slot.
puts “*** Configuring #{owner} as the slot owner”
owner.r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”stable”)
owner.r.cluster(“addslots”,slot)
# Make sure this information will propagate. Not strictly needed
# since there is no past owner, so all the other nodes will accept
# whatever epoch this node will claim the slot with.
owner.r.cluster(“bumpepoch”)
# Remove the owner from the list of migrating/importing
# nodes.
migrating.delete(owner)
importing.delete(owner)
end
# If there are multiple owners of the slot, we need to fix it
# so that a single node is the owner and all the other nodes
# are in importing state. Later the fix can be handled by one
# of the base cases above.
#
# Note that this case also covers multiple nodes having the slot
# in migrating state, since migrating is a valid state only for
# slot owners.
if owners.length > 1
owner = get_node_with_most_keys_in_slot(owners,slot)
owners.each{|n|
next if n == owner
n.r.cluster(‘delslots’,slot)
n.r.cluster(‘setslot’,slot,’importing’,owner.info[:name])
importing.delete(n) # Avoid duplciates
importing << n
}
owner.r.cluster(‘bumpepoch’)
end
# Case 1: The slot is in migrating state in one slot, and in
# importing state in 1 slot. That’s trivial to address.
if migrating.length == 1 && importing.length == 1
move_slot(migrating[0],importing[0],slot,:dots=>true,:fix=>true)
# Case 2: There are multiple nodes that claim the slot as importing,
# they probably got keys about the slot after a restart so opened
# the slot. In this case we just move all the keys to the owner
# according to the configuration.
elsif migrating.length == 0 && importing.length > 0
xputs “>>> Moving all the #{slot} slot keys to its owner #{owner}”
importing.each {|node|
next if node == owner
move_slot(node,owner,slot,:dots=>true,:fix=>true,:cold=>true)
xputs “>>> Setting #{slot} as STABLE in #{node}”
node.r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”stable”)
}
# Case 3: There are no slots claiming to be in importing state, but
# there is a migrating node that actually don’t have any key. We
# can just close the slot, probably a reshard interrupted in the middle.
elsif importing.length == 0 && migrating.length == 1 &&
migrating[0].r.cluster(“getkeysinslot”,slot,10).length == 0
migrating[0].r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”stable”)
else
xputs “[ERR] Sorry, Redis-trib can’t fix this slot yet (work in progress). Slot is set as migrating in #{migrating.join(“,”)}, as importing in #{importing.join(“,”)}, owner is #{owner}”
end
end
# Check if all the nodes agree about the cluster configuration
def check_config_consistency
if !is_config_consistent?
cluster_error “[ERR] Nodes don’t agree about configuration!”
else
xputs “[OK] All nodes agree about slots configuration.”
end
end
def is_config_consistent?
signatures=[]
@nodes.each{|n|
signatures << n.get_config_signature
}
return signatures.uniq.length == 1
end
def wait_cluster_join
print “Waiting for the cluster to join”
while !is_config_consistent?
print “.”
STDOUT.flush
sleep 1
end
print “\n”
end
def alloc_slots
nodes_count = @nodes.length
masters_count = @nodes.length / (@replicas+1)
masters = []
# The first step is to split instances by IP. This is useful as
# we’ll try to allocate master nodes in different physical machines
# (as much as possible) and to allocate slaves of a given master in
# different physical machines as well.
#
# This code assumes just that if the IP is different, than it is more
# likely that the instance is running in a different physical host
# or at least a different virtual machine.
ips = {}
@nodes.each{|n|
ips[n.info[:host]] = [] if !ips[n.info[:host]]
ips[n.info[:host]] << n
}
# Select master instances
puts “Using #{masters_count} masters:”
interleaved = []
stop = false
while not stop do
# Take one node from each IP until we run out of nodes
# across every IP.
ips.each do |ip,nodes|
if nodes.empty?
# if this IP has no remaining nodes, check for termination
if interleaved.length == nodes_count
# stop when ‘interleaved’ has accumulated all nodes
stop = true
next
end
else
# else, move one node from this IP to ‘interleaved’
interleaved.push nodes.shift
end
end
end
masters = interleaved.slice!(0, masters_count)
nodes_count -= masters.length
masters.each{|m| puts m}
# Alloc slots on masters
slots_per_node = ClusterHashSlots.to_f / masters_count
first = 0
cursor = 0.0
masters.each_with_index{|n,masternum|
last = (cursor+slots_per_node-1).round
if last > ClusterHashSlots || masternum == masters.length-1
last = ClusterHashSlots-1
end
last = first if last < first # Min step is 1.
n.add_slots first..last
first = last+1
cursor += slots_per_node
}
# Select N replicas for every master.
# We try to split the replicas among all the IPs with spare nodes
# trying to avoid the host where the master is running, if possible.
#
# Note we loop two times. The first loop assigns the requested
# number of replicas to each master. The second loop assigns any
# remaining instances as extra replicas to masters. Some masters
# may end up with more than their requested number of replicas, but
# all nodes will be used.
assignment_verbose = false
[:requested,:unused].each do |assign|
masters.each do |m|
assigned_replicas = 0
while assigned_replicas < @replicas
break if nodes_count == 0
if assignment_verbose
if assign == :requested
puts “Requesting total of #{@replicas} replicas ” \
“(#{assigned_replicas} replicas assigned ” \
“so far with #{nodes_count} total remaining).”
elsif assign == :unused
puts “Assigning extra instance to replication ” \
“role too (#{nodes_count} remaining).”
end
end
# Return the first node not matching our current master
node = interleaved.find{|n| n.info[:host] != m.info[:host]}
# If we found a node, use it as a best-first match.
# Otherwise, we didn’t find a node on a different IP, so we
# go ahead and use a same-IP replica.
if node
slave = node
interleaved.delete node
else
slave = interleaved.shift
end
slave.set_as_replica(m.info[:name])
nodes_count -= 1
assigned_replicas += 1
puts “Adding replica #{slave} to #{m}”
# If we are in the “assign extra nodes” loop,
# we want to assign one extra replica to each
# master before repeating masters.
# This break lets us assign extra replicas to masters
# in a round-robin way.
break if assign == :unused
end
end
end
end
def flush_nodes_config
@nodes.each{|n|
n.flush_node_config
}
end
def show_nodes
@nodes.each{|n|
xputs n.info_string
}
end
# Redis Cluster config epoch collision resolution code is able to eventually
# set a different epoch to each node after a new cluster is created, but
# it is slow compared to assign a progressive config epoch to each node
# before joining the cluster. However we do just a best-effort try here
# since if we fail is not a problem.
def assign_config_epoch
config_epoch = 1
@nodes.each{|n|
begin
n.r.cluster(“set-config-epoch”,config_epoch)
rescue
end
config_epoch += 1
}
end
def join_cluster
# We use a brute force approach to make sure the node will meet
# each other, that is, sending CLUSTER MEET messages to all the nodes
# about the very same node.
# Thanks to gossip this information should propagate across all the
# cluster in a matter of seconds.
first = false
@nodes.each{|n|
if !first then first = n.info; next; end # Skip the first node
n.r.cluster(“meet”,first[:host],first[:port])
}
end
def yes_or_die(msg)
print “#{msg} (type ‘yes’ to accept): ”
STDOUT.flush
if !(STDIN.gets.chomp.downcase == “yes”)
xputs “*** Aborting…”
exit 1
end
end
def load_cluster_info_from_node(nodeaddr)
node = ClusterNode.new(nodeaddr)
node.connect(:abort => true)
node.assert_cluster
node.load_info(:getfriends => true)
add_node(node)
node.friends.each{|f|
next if f[:flags].index(“noaddr”) ||
f[:flags].index(“disconnected”) ||
f[:flags].index(“fail”)
fnode = ClusterNode.new(f[:addr])
fnode.connect()
next if !fnode.r
begin
fnode.load_info()
add_node(fnode)
rescue => e
xputs “[ERR] Unable to load info for node #{fnode}”
end
}
populate_nodes_replicas_info
end
# This function is called by load_cluster_info_from_node in order to
# add additional information to every node as a list of replicas.
def populate_nodes_replicas_info
# Start adding the new field to every node.
@nodes.each{|n|
n.info[:replicas] = []
}
# Populate the replicas field using the replicate field of slave
# nodes.
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.info[:replicate]
master = get_node_by_name(n.info[:replicate])
if !master
xputs “*** WARNING: #{n} claims to be slave of unknown node ID #{n.info[:replicate]}.”
else
master.info[:replicas] << n
end
end
}
end
# Given a list of source nodes return a “resharding plan”
# with what slots to move in order to move “numslots” slots to another
# instance.
def compute_reshard_table(sources,numslots)
moved = []
# Sort from bigger to smaller instance, for two reasons:
# 1) If we take less slots than instances it is better to start
# getting from the biggest instances.
# 2) We take one slot more from the first instance in the case of not
# perfect divisibility. Like we have 3 nodes and need to get 10
# slots, we take 4 from the first, and 3 from the rest. So the
# biggest is always the first.
sources = sources.sort{|a,b| b.slots.length <=> a.slots.length}
source_tot_slots = sources.inject(0) {|sum,source|
sum+source.slots.length
}
sources.each_with_index{|s,i|
# Every node will provide a number of slots proportional to the
# slots it has assigned.
n = (numslots.to_f/source_tot_slots*s.slots.length)
if i == 0
n = n.ceil
else
n = n.floor
end
s.slots.keys.sort[(0…n)].each{|slot|
if moved.length < numslots
moved << {:source => s, :slot => slot}
end
}
}
return moved
end
def show_reshard_table(table)
table.each{|e|
puts ” Moving slot #{e[:slot]} from #{e[:source].info[:name]}”
}
end
# Move slots between source and target nodes using MIGRATE.
#
# Options:
# :verbose — Print a dot for every moved key.
# :fix — We are moving in the context of a fix. Use REPLACE.
# :cold — Move keys without opening slots / reconfiguring the nodes.
# :update — Update nodes.info[:slots] for source/target nodes.
# :quiet — Don’t print info messages.
def move_slot(source,target,slot,o={})
o = {:pipeline => MigrateDefaultPipeline}.merge(o)
# We start marking the slot as importing in the destination node,
# and the slot as migrating in the target host. Note that the order of
# the operations is important, as otherwise a client may be redirected
# to the target node that does not yet know it is importing this slot.
if !o[:quiet]
print “Moving slot #{slot} from #{source} to #{target}: ”
STDOUT.flush
end
if !o[:cold]
target.r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”importing”,source.info[:name])
source.r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”migrating”,target.info[:name])
end
# Migrate all the keys from source to target using the MIGRATE command
while true
keys = source.r.cluster(“getkeysinslot”,slot,o[:pipeline])
break if keys.length == 0
begin
source.r.client.call([“migrate”,target.info[:host],target.info[:port],””,0,@timeout,:keys,*keys])
rescue => e
if o[:fix] && e.to_s =~ /BUSYKEY/
xputs “*** Target key exists. Replacing it for FIX.”
source.r.client.call([“migrate”,target.info[:host],target.info[:port],””,0,@timeout,:replace,:keys,*keys])
else
puts “”
xputs “[ERR] Calling MIGRATE: #{e}”
exit 1
end
end
print “.”*keys.length if o[:dots]
STDOUT.flush
end
puts if !o[:quiet]
# Set the new node as the owner of the slot in all the known nodes.
if !o[:cold]
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.has_flag?(“slave”)
n.r.cluster(“setslot”,slot,”node”,target.info[:name])
}
end
# Update the node logical config
if o[:update] then
source.info[:slots].delete(slot)
target.info[:slots][slot] = true
end
end
# redis-trib subcommands implementations.
def check_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
check_cluster
end
def info_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
show_cluster_info
end
def rebalance_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
opt = {
‘pipeline’ => MigrateDefaultPipeline,
‘threshold’ => RebalanceDefaultThreshold
}.merge(opt)
# Load nodes info before parsing options, otherwise we can’t
# handle –weight.
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
# Options parsing
threshold = opt[‘threshold’].to_i
autoweights = opt[‘auto-weights’]
weights = {}
opt[‘weight’].each{|w|
fields = w.split(“=”)
node = get_node_by_abbreviated_name(fields[0])
if !node || !node.has_flag?(“master”)
puts “*** No such master node #{fields[0]}”
exit 1
end
weights[node.info[:name]] = fields[1].to_f
} if opt[‘weight’]
useempty = opt[‘use-empty-masters’]
# Assign a weight to each node, and compute the total cluster weight.
total_weight = 0
nodes_involved = 0
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.has_flag?(“master”)
next if !useempty && n.slots.length == 0
n.info[:w] = weights[n.info[:name]] ? weights[n.info[:name]] : 1
total_weight += n.info[:w]
nodes_involved += 1
end
}
# Check cluster, only proceed if it looks sane.
check_cluster(:quiet => true)
if @errors.length != 0
puts “*** Please fix your cluster problems before rebalancing”
exit 1
end
# Calculate the slots balance for each node. It’s the number of
# slots the node should lose (if positive) or gain (if negative)
# in order to be balanced.
threshold = opt[‘threshold’].to_f
threshold_reached = false
@nodes.each{|n|
if n.has_flag?(“master”)
next if !n.info[:w]
expected = ((ClusterHashSlots.to_f / total_weight) *
n.info[:w]).to_i
n.info[:balance] = n.slots.length – expected
# Compute the percentage of difference between the
# expected number of slots and the real one, to see
# if it’s over the threshold specified by the user.
over_threshold = false
if threshold > 0
if n.slots.length > 0
err_perc = (100-(100.0*expected/n.slots.length)).abs
over_threshold = true if err_perc > threshold
elsif expected > 0
over_threshold = true
end
end
threshold_reached = true if over_threshold
end
}
if !threshold_reached
xputs “*** No rebalancing needed! All nodes are within the #{threshold}% threshold.”
return
end
# Only consider nodes we want to change
sn = @nodes.select{|n|
n.has_flag?(“master”) && n.info[:w]
}
# Because of rounding, it is possible that the balance of all nodes
# summed does not give 0. Make sure that nodes that have to provide
# slots are always matched by nodes receiving slots.
total_balance = sn.map{|x| x.info[:balance]}.reduce{|a,b| a+b}
while total_balance > 0
sn.each{|n|
if n.info[:balance] < 0 && total_balance > 0
n.info[:balance] -= 1
total_balance -= 1
end
}
end
# Sort nodes by their slots balance.
sn = sn.sort{|a,b|
a.info[:balance] <=> b.info[:balance]
}
xputs “>>> Rebalancing across #{nodes_involved} nodes. Total weight = #{total_weight}”
if $verbose
sn.each{|n|
puts “#{n} balance is #{n.info[:balance]} slots”
}
end
# Now we have at the start of the ‘sn’ array nodes that should get
# slots, at the end nodes that must give slots.
# We take two indexes, one at the start, and one at the end,
# incrementing or decrementing the indexes accordingly til we
# find nodes that need to get/provide slots.
dst_idx = 0
src_idx = sn.length – 1
while dst_idx < src_idx
dst = sn[dst_idx]
src = sn[src_idx]
numslots = [dst.info[:balance],src.info[:balance]].map{|n|
n.abs
}.min
if numslots > 0
puts “Moving #{numslots} slots from #{src} to #{dst}”
# Actaully move the slots.
reshard_table = compute_reshard_table([src],numslots)
if reshard_table.length != numslots
xputs “*** Assertio failed: Reshard table != number of slots”
exit 1
end
if opt[‘simulate’]
print “#”*reshard_table.length
else
reshard_table.each{|e|
move_slot(e[:source],dst,e[:slot],
:quiet=>true,
:dots=>false,
:update=>true,
:pipeline=>opt[‘pipeline’])
print “#”
STDOUT.flush
}
end
puts
end
# Update nodes balance.
dst.info[:balance] += numslots
src.info[:balance] -= numslots
dst_idx += 1 if dst.info[:balance] == 0
src_idx -= 1 if src.info[:balance] == 0
end
end
def fix_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
@fix = true
@timeout = opt[‘timeout’].to_i if opt[‘timeout’]
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
check_cluster
end
def reshard_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
opt = {‘pipeline’ => MigrateDefaultPipeline}.merge(opt)
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
check_cluster
if @errors.length != 0
puts “*** Please fix your cluster problems before resharding”
exit 1
end
@timeout = opt[‘timeout’].to_i if opt[‘timeout’].to_i
# Get number of slots
if opt[‘slots’]
numslots = opt[‘slots’].to_i
else
numslots = 0
while numslots <= 0 or numslots > ClusterHashSlots
print “How many slots do you want to move (from 1 to #{ClusterHashSlots})? ”
numslots = STDIN.gets.to_i
end
end
# Get the target instance
if opt[‘to’]
target = get_node_by_name(opt[‘to’])
if !target || target.has_flag?(“slave”)
xputs “*** The specified node is not known or not a master, please retry.”
exit 1
end
else
target = nil
while not target
print “What is the receiving node ID? ”
target = get_node_by_name(STDIN.gets.chop)
if !target || target.has_flag?(“slave”)
xputs “*** The specified node is not known or not a master, please retry.”
target = nil
end
end
end
# Get the source instances
sources = []
if opt[‘from’]
opt[‘from’].split(‘,’).each{|node_id|
if node_id == “all”
sources = “all”
break
end
src = get_node_by_name(node_id)
if !src || src.has_flag?(“slave”)
xputs “*** The specified node is not known or is not a master, please retry.”
exit 1
end
sources << src
}
else
xputs “Please enter all the source node IDs.”
xputs ” Type ‘all’ to use all the nodes as source nodes for the hash slots.”
xputs ” Type ‘done’ once you entered all the source nodes IDs.”
while true
print “Source node ##{sources.length+1}:”
line = STDIN.gets.chop
src = get_node_by_name(line)
if line == “done”
break
elsif line == “all”
sources = “all”
break
elsif !src || src.has_flag?(“slave”)
xputs “*** The specified node is not known or is not a master, please retry.”
elsif src.info[:name] == target.info[:name]
xputs “*** It is not possible to use the target node as source node.”
else
sources << src
end
end
end
if sources.length == 0
puts “*** No source nodes given, operation aborted”
exit 1
end
# Handle soures == all.
if sources == “all”
sources = []
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n.info[:name] == target.info[:name]
next if n.has_flag?(“slave”)
sources << n
}
end
# Check if the destination node is the same of any source nodes.
if sources.index(target)
xputs “*** Target node is also listed among the source nodes!”
exit 1
end
puts “\nReady to move #{numslots} slots.”
puts ” Source nodes:”
sources.each{|s| puts ” “+s.info_string}
puts ” Destination node:”
puts ” #{target.info_string}”
reshard_table = compute_reshard_table(sources,numslots)
puts ” Resharding plan:”
show_reshard_table(reshard_table)
if !opt[‘yes’]
print “Do you want to proceed with the proposed reshard plan (yes/no)? ”
yesno = STDIN.gets.chop
exit(1) if (yesno != “yes”)
end
reshard_table.each{|e|
move_slot(e[:source],target,e[:slot],
:dots=>true,
:pipeline=>opt[‘pipeline’])
}
end
# This is an helper function for create_cluster_cmd that verifies if
# the number of nodes and the specified replicas have a valid configuration
# where there are at least three master nodes and enough replicas per node.
def check_create_parameters
masters = @nodes.length/(@replicas+1)
if masters < 3
puts “*** ERROR: Invalid configuration for cluster creation.”
puts “*** Redis Cluster requires at least 3 master nodes.”
puts “*** This is not possible with #{@nodes.length} nodes and #{@replicas} replicas per node.”
puts “*** At least #{3*(@replicas+1)} nodes are required.”
exit 1
end
end
def create_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
opt = {‘replicas’ => 0}.merge(opt)
@replicas = opt[‘replicas’].to_i
xputs “>>> Creating cluster”
argv[0..-1].each{|n|
node = ClusterNode.new(n)
node.connect(:abort => true)
node.assert_cluster
node.load_info
node.assert_empty
add_node(node)
}
check_create_parameters
xputs “>>> Performing hash slots allocation on #{@nodes.length} nodes…”
alloc_slots
show_nodes
yes_or_die “Can I set the above configuration?”
flush_nodes_config
xputs “>>> Nodes configuration updated”
xputs “>>> Assign a different config epoch to each node”
assign_config_epoch
xputs “>>> Sending CLUSTER MEET messages to join the cluster”
join_cluster
# Give one second for the join to start, in order to avoid that
# wait_cluster_join will find all the nodes agree about the config as
# they are still empty with unassigned slots.
sleep 1
wait_cluster_join
flush_nodes_config # Useful for the replicas
check_cluster
end
def addnode_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
xputs “>>> Adding node #{argv[0]} to cluster #{argv[1]}”
# Check the existing cluster
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[1])
check_cluster
# If –master-id was specified, try to resolve it now so that we
# abort before starting with the node configuration.
if opt[‘slave’]
if opt[‘master-id’]
master = get_node_by_name(opt[‘master-id’])
if !master
xputs “[ERR] No such master ID #{opt[‘master-id’]}”
end
else
master = get_master_with_least_replicas
xputs “Automatically selected master #{master}”
end
end
# Add the new node
new = ClusterNode.new(argv[0])
new.connect(:abort => true)
new.assert_cluster
new.load_info
new.assert_empty
first = @nodes.first.info
add_node(new)
# Send CLUSTER MEET command to the new node
xputs “>>> Send CLUSTER MEET to node #{new} to make it join the cluster.”
new.r.cluster(“meet”,first[:host],first[:port])
# Additional configuration is needed if the node is added as
# a slave.
if opt[‘slave’]
wait_cluster_join
xputs “>>> Configure node as replica of #{master}.”
new.r.cluster(“replicate”,master.info[:name])
end
xputs “[OK] New node added correctly.”
end
def delnode_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
id = argv[1].downcase
xputs “>>> Removing node #{id} from cluster #{argv[0]}”
# Load cluster information
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
# Check if the node exists and is not empty
node = get_node_by_name(id)
if !node
xputs “[ERR] No such node ID #{id}”
exit 1
end
if node.slots.length != 0
xputs “[ERR] Node #{node} is not empty! Reshard data away and try again.”
exit 1
end
# Send CLUSTER FORGET to all the nodes but the node to remove
xputs “>>> Sending CLUSTER FORGET messages to the cluster…”
@nodes.each{|n|
next if n == node
if n.info[:replicate] && n.info[:replicate].downcase == id
# Reconfigure the slave to replicate with some other node
master = get_master_with_least_replicas
xputs “>>> #{n} as replica of #{master}”
n.r.cluster(“replicate”,master.info[:name])
end
n.r.cluster(“forget”,argv[1])
}
# Finally shutdown the node
xputs “>>> SHUTDOWN the node.”
node.r.shutdown
end
def set_timeout_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
timeout = argv[1].to_i
if timeout < 100
puts “Setting a node timeout of less than 100 milliseconds is a bad idea.”
exit 1
end
# Load cluster information
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
ok_count = 0
err_count = 0
# Send CLUSTER FORGET to all the nodes but the node to remove
xputs “>>> Reconfiguring node timeout in every cluster node…”
@nodes.each{|n|
begin
n.r.config(“set”,”cluster-node-timeout”,timeout)
n.r.config(“rewrite”)
ok_count += 1
xputs “*** New timeout set for #{n}”
rescue => e
puts “ERR setting node-timeot for #{n}: #{e}”
err_count += 1
end
}
xputs “>>> New node timeout set. #{ok_count} OK, #{err_count} ERR.”
end
def call_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
cmd = argv[1..-1]
cmd[0] = cmd[0].upcase
# Load cluster information
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
xputs “>>> Calling #{cmd.join(” “)}”
@nodes.each{|n|
begin
res = n.r.send(*cmd)
puts “#{n}: #{res}”
rescue => e
puts “#{n}: #{e}”
end
}
end
def import_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
source_addr = opt[‘from’]
xputs “>>> Importing data from #{source_addr} to cluster #{argv[1]}”
use_copy = opt[‘copy’]
use_replace = opt[‘replace’]
# Check the existing cluster.
load_cluster_info_from_node(argv[0])
check_cluster
# Connect to the source node.
xputs “>>> Connecting to the source Redis instance”
src_host,src_port = source_addr.split(“:”)
source = Redis.new(:host =>src_host, :port =>src_port)
if source.info[‘cluster_enabled’].to_i == 1
xputs “[ERR] The source node should not be a cluster node.”
end
xputs “*** Importing #{source.dbsize} keys from DB 0”
# Build a slot -> node map
slots = {}
@nodes.each{|n|
n.slots.each{|s,_|
slots[s] = n
}
}
# Use SCAN to iterate over the keys, migrating to the
# right node as needed.
cursor = nil
while cursor != 0
cursor,keys = source.scan(cursor, :count => 1000)
cursor = cursor.to_i
keys.each{|k|
# Migrate keys using the MIGRATE command.
slot = key_to_slot(k)
target = slots[slot]
print “Migrating #{k} to #{target}: ”
STDOUT.flush
begin
cmd = [“migrate”,target.info[:host],target.info[:port],k,0,@timeout]
cmd << :copy if use_copy
cmd << :replace if use_replace
source.client.call(cmd)
rescue => e
puts e
else
puts “OK”
end
}
end
end
def help_cluster_cmd(argv,opt)
show_help
exit 0
end
# Parse the options for the specific command “cmd”.
# Returns an hash populate with option => value pairs, and the index of
# the first non-option argument in ARGV.
def parse_options(cmd)
idx = 1 ; # Current index into ARGV
options={}
while idx < ARGV.length && ARGV[idx][0..1] == ‘–‘
if ARGV[idx][0..1] == “–”
option = ARGV[idx][2..-1]
idx += 1
# –verbose is a global option
if option == “verbose”
$verbose = true
next
end
if ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd] == nil || ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd][option] == nil
puts “Unknown option ‘#{option}’ for command ‘#{cmd}'”
exit 1
end
if ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd][option] != false
value = ARGV[idx]
idx += 1
else
value = true
end
# If the option is set to [], it’s a multiple arguments
# option. We just queue every new value into an array.
if ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd][option] == []
options[option] = [] if !options[option]
options[option] << value
else
options[option] = value
end
else
# Remaining arguments are not options.
break
end
end
# Enforce mandatory options
if ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd]
ALLOWED_OPTIONS[cmd].each {|option,val|
if !options[option] && val == :required
puts “Option ‘–#{option}’ is required “+ \
“for subcommand ‘#{cmd}'”
exit 1
end
}
end
return options,idx
end
end
#################################################################################
# Libraries
#
# We try to don’t depend on external libs since this is a critical part
# of Redis Cluster.
#################################################################################
# This is the CRC16 algorithm used by Redis Cluster to hash keys.
# Implementation according to CCITT standards.
#
# This is actually the XMODEM CRC 16 algorithm, using the
# following parameters:
#
# Name : “XMODEM”, also known as “ZMODEM”, “CRC-16/ACORN”
# Width : 16 bit
# Poly : 1021 (That is actually x^16 + x^12 + x^5 + 1)
# Initialization : 0000
# Reflect Input byte : False
# Reflect Output CRC : False
# Xor constant to output CRC : 0000
# Output for “123456789” : 31C3
module RedisClusterCRC16
def RedisClusterCRC16.crc16(bytes)
crc = 0
bytes.each_byte{|b|
crc = ((crc<<8) & 0xffff) ^ XMODEMCRC16Lookup[((crc>>8)^b) & 0xff]
}
crc
end
private
XMODEMCRC16Lookup = [
0x0000,0x1021,0x2042,0x3063,0x4084,0x50a5,0x60c6,0x70e7,
0x8108,0x9129,0xa14a,0xb16b,0xc18c,0xd1ad,0xe1ce,0xf1ef,
0x1231,0x0210,0x3273,0x2252,0x52b5,0x4294,0x72f7,0x62d6,
0x9339,0x8318,0xb37b,0xa35a,0xd3bd,0xc39c,0xf3ff,0xe3de,
0x2462,0x3443,0x0420,0x1401,0x64e6,0x74c7,0x44a4,0x5485,
0xa56a,0xb54b,0x8528,0x9509,0xe5ee,0xf5cf,0xc5ac,0xd58d,
0x3653,0x2672,0x1611,0x0630,0x76d7,0x66f6,0x5695,0x46b4,
0xb75b,0xa77a,0x9719,0x8738,0xf7df,0xe7fe,0xd79d,0xc7bc,
0x48c4,0x58e5,0x6886,0x78a7,0x0840,0x1861,0x2802,0x3823,
0xc9cc,0xd9ed,0xe98e,0xf9af,0x8948,0x9969,0xa90a,0xb92b,
0x5af5,0x4ad4,0x7ab7,0x6a96,0x1a71,0x0a50,0x3a33,0x2a12,
0xdbfd,0xcbdc,0xfbbf,0xeb9e,0x9b79,0x8b58,0xbb3b,0xab1a,
0x6ca6,0x7c87,0x4ce4,0x5cc5,0x2c22,0x3c03,0x0c60,0x1c41,
0xedae,0xfd8f,0xcdec,0xddcd,0xad2a,0xbd0b,0x8d68,0x9d49,
0x7e97,0x6eb6,0x5ed5,0x4ef4,0x3e13,0x2e32,0x1e51,0x0e70,
0xff9f,0xefbe,0xdfdd,0xcffc,0xbf1b,0xaf3a,0x9f59,0x8f78,
0x9188,0x81a9,0xb1ca,0xa1eb,0xd10c,0xc12d,0xf14e,0xe16f,
0x1080,0x00a1,0x30c2,0x20e3,0x5004,0x4025,0x7046,0x6067,
0x83b9,0x9398,0xa3fb,0xb3da,0xc33d,0xd31c,0xe37f,0xf35e,
0x02b1,0x1290,0x22f3,0x32d2,0x4235,0x5214,0x6277,0x7256,
0xb5ea,0xa5cb,0x95a8,0x8589,0xf56e,0xe54f,0xd52c,0xc50d,
0x34e2,0x24c3,0x14a0,0x0481,0x7466,0x6447,0x5424,0x4405,
0xa7db,0xb7fa,0x8799,0x97b8,0xe75f,0xf77e,0xc71d,0xd73c,
0x26d3,0x36f2,0x0691,0x16b0,0x6657,0x7676,0x4615,0x5634,
0xd94c,0xc96d,0xf90e,0xe92f,0x99c8,0x89e9,0xb98a,0xa9ab,
0x5844,0x4865,0x7806,0x6827,0x18c0,0x08e1,0x3882,0x28a3,
0xcb7d,0xdb5c,0xeb3f,0xfb1e,0x8bf9,0x9bd8,0xabbb,0xbb9a,
0x4a75,0x5a54,0x6a37,0x7a16,0x0af1,0x1ad0,0x2ab3,0x3a92,
0xfd2e,0xed0f,0xdd6c,0xcd4d,0xbdaa,0xad8b,0x9de8,0x8dc9,
0x7c26,0x6c07,0x5c64,0x4c45,0x3ca2,0x2c83,0x1ce0,0x0cc1,
0xef1f,0xff3e,0xcf5d,0xdf7c,0xaf9b,0xbfba,0x8fd9,0x9ff8,
0x6e17,0x7e36,0x4e55,0x5e74,0x2e93,0x3eb2,0x0ed1,0x1ef0
]
end
# Turn a key name into the corrisponding Redis Cluster slot.
def key_to_slot(key)
# Only hash what is inside {…} if there is such a pattern in the key.
# Note that the specification requires the content that is between
# the first { and the first } after the first {. If we found {} without
# nothing in the middle, the whole key is hashed as usually.
s = key.index “{”
if s
e = key.index “}”,s+1
if e && e != s+1
key = key[s+1..e-1]
end
end
RedisClusterCRC16.crc16(key) % 16384
end
#################################################################################
# Definition of commands
#################################################################################
COMMANDS={
“create” => [“create_cluster_cmd”, -2, “host1:port1 … hostN:portN”],
“check” => [“check_cluster_cmd”, 2, “host:port”],
“info” => [“info_cluster_cmd”, 2, “host:port”],
“fix” => [“fix_cluster_cmd”, 2, “host:port”],
“reshard” => [“reshard_cluster_cmd”, 2, “host:port”],
“rebalance” => [“rebalance_cluster_cmd”, -2, “host:port”],
“add-node” => [“addnode_cluster_cmd”, 3, “new_host:new_port existing_host:existing_port”],
“del-node” => [“delnode_cluster_cmd”, 3, “host:port node_id”],
“set-timeout” => [“set_timeout_cluster_cmd”, 3, “host:port milliseconds”],
“call” => [“call_cluster_cmd”, -3, “host:port command arg arg .. arg”],
“import” => [“import_cluster_cmd”, 2, “host:port”],
“help” => [“help_cluster_cmd”, 1, “(show this help)”]
}
ALLOWED_OPTIONS={
“create” => {“replicas” => true},
“add-node” => {“slave” => false, “master-id” => true},
“import” => {“from” => :required, “copy” => false, “replace” => false},
“reshard” => {“from” => true, “to” => true, “slots” => true, “yes” => false, “timeout” => true, “pipeline” => true},
“rebalance” => {“weight” => [], “auto-weights” => false, “use-empty-masters” => false, “timeout” => true, “simulate” => false, “pipeline” => true, “threshold” => true},
“fix” => {“timeout” => MigrateDefaultTimeout},
}
def show_help
puts “Usage: redis-trib <command> <options> <arguments …>\n\n”
COMMANDS.each{|k,v|
o = “”
puts ” #{k.ljust(15)} #{v[2]}”
if ALLOWED_OPTIONS[k]
ALLOWED_OPTIONS[k].each{|optname,has_arg|
puts ” –#{optname}” + (has_arg ? ” <arg>” : “”)
}
end
}
puts “\nFor check, fix, reshard, del-node, set-timeout you can specify the host and port of any working node in the cluster.\n”
end
# Sanity check
if ARGV.length == 0
show_help
exit 1
end
rt = RedisTrib.new
cmd_spec = COMMANDS[ARGV[0].downcase]
if !cmd_spec
puts “Unknown redis-trib subcommand ‘#{ARGV[0]}'”
exit 1
end
# Parse options
cmd_options,first_non_option = rt.parse_options(ARGV[0].downcase)
rt.check_arity(cmd_spec[1],ARGV.length-(first_non_option-1))
# Dispatch
rt.send(cmd_spec[0],ARGV[first_non_option..-1],cmd_options)
总结
到此这篇关于window下创建redis出现问题小结的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关创建redis出现问题内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!

