Redis分布式限流组件设计与使用实例
本文主要讲解基于 自定义注解+Aop+反射+Redis+Lua表达式 实现的限流设计方案。实现的限流设计与实际使用。
1.背景
在互联网开发中经常遇到需要限流的场景一般分为两种
- 业务场景需要(比如:5分钟内发送验证码不超过次);
- 对流量大的功能流量削峰;
一般我们衡量系统处理能力的指标是每秒的QPS或者TPS,假设系统每秒的流量阈值是2000,
理论上第2001个请求进来时,那么这个请求就需要被限流。
本文演示项目使用的是 SpringBoot 项目,项目构建以及其他配置,这里不做演示。文末附限流Demo源码
2.Redis计数器限流设计
本文演示项目使用的是 SpringBoot 项目,这里仅挑选了重点实现代码展示,
项目构建以及其他配置,这里不做演示,详细配置请参考源码demo工程。
2.1Lua脚本
Lua 是一种轻量小巧的脚本语言可以理解为就是一组命令。
使用Redis的计数器达到限流的效果,表面上Redis自带命令多个组合也可以支持了,那为什么还要用Lua呢?
因为要保证原子性,这也是使用redis+Lua表达式原因,一组命令要么全成功,要么全失败。
相比Redis事务,Lua脚本的优点:
- 减少网络开销:多个请求通过脚本一次发送,减少网络延迟
- 原子操作:将脚本作为一个整体执行,中间不会插入其他命令,无需使用事务
- 复用:客户端发送的脚本永久存在redis中,其他客户端可以复用脚本
- 可嵌入性:可嵌入JAVA,C#等多种编程语言,支持不同操作系统跨平台交互
实现限流Lua脚本示例
# 定义计数变量
local count
# 获取调用脚本时传入的第一个key值(用作限流的 key)
count = redis.call(‘get’,KEYS[1])
# 限流最大值比较,若超过最大值,则直接返回
if count and tonumber(count) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then
return count;
end
# incr 命令 执行计算器累加
count = redis.call(‘incr’,KEYS[1])
# 从第一次调用开始限流,并设置失效时间
if tonumber(count) == 1 then
redis.call(‘expire’,KEYS[1],ARGV[2])
end
return count;
参数说明
- KEYS[1] – redis的Key
- ARGV[1] – 限流次数
- ARGV[2] – 失效时间
2.2自定义注解
支持范围:任意接口
/**
* 描述: 限流注解
*
* @author 程序员小强
**/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RateLimit {
/**
* 限流唯一标示 key
* 若同时使用 keyFiled 则当前 key作为前缀
*/
String key();
/**
* 限流时间-单位:秒数
* 默认 60s
*/
int time() default 60;
/**
* 限流次数
* 失效时间段内最大放行次数
*/
int count();
/**
* 可作为限流key-参数类中属性名,动态值
* 示例:phone、userId 等
*/
String keyField() default "";
/**
* 超过最大访问次数后的,提示内容
*/
String msg() default "over the max request times please try again";
}
属性介绍
- key – 必填,限流key唯一标识,redis存储key
- time -过期时间,单位 秒,默认60s
- count – 必填,失效时间段内最大放行次数
- keyField – 动态限流key,比如参数是一个自定义的类,里面有属性userId 等。可以使用keyField=“userId”,
这样生成的key为参数中userId的值。一般与key属性组合使用。不支持java基本类型参数,
仅支持参数是一个对象的接口。
msg – 超过限流的提示内容
示例:
@RateLimit(key = "limit-phone-key", time = 300, count = 10, keyField = "phone", msg = "5分钟内,验证码最多发送10次")
含义 – 5分钟内根据手机号限流10次
RedisKey- limit-phone-key:后面拼接的是参数中phone的值。
2.3限流组件
这里用的是jedis客户端,配置就不列在这里的,详见源码,文末附源码地址
/**
* Redis限流组件
*
* @author 程序员小强
*/
@Component
public class RedisRateLimitComponent {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisRateLimitComponent.class);
private JedisPool jedisPool;
@Autowired
public RedisRateLimitComponent(JedisPool jedisPool) {
this.jedisPool = jedisPool;
}
/**
* 限流方法
* 1.执行 lua 表达式
* 2.通过 lua 表达式实现-限流计数器
*
* @param redisKey
* @param time 超时时间-秒数
* @param rateLimitCount 限流次数
*/
public Long rateLimit(String redisKey, Integer time, Integer rateLimitCount) {
Jedis jedis = null;
try {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
Object obj = jedis.evalsha(jedis.scriptLoad(this.buildLuaScript()), Collections.singletonList(redisKey),
Arrays.asList(String.valueOf(rateLimitCount), String.valueOf(time)));
return Long.valueOf(obj.toString());
} catch (JedisException ex) {
logger.error("[ executeLua ] >> messages:{}", ex.getMessage(), ex);
throw new RateLimitException("[ RedisRateLimitComponent ] >> jedis run lua script exception" + ex.getMessage());
} finally {
if (jedis != null) {
if (jedis.isConnected()) {
jedis.close();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 构建lua 表达式
* KEYS[1] -- 参数key
* ARGV[1]-- 失效时间段内最大放行次数
* ARGV[2]-- 失效时间|秒
*/
private String buildLuaScript() {
StringBuilder luaBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//定义变量
luaBuilder.append("local count");
//获取调用脚本时传入的第一个key值(用作限流的 key)
luaBuilder.append("\ncount = redis.call('get',KEYS[1])");
// 获取调用脚本时传入的第一个参数值(限流大小)-- 调用不超过最大值,则直接返回
luaBuilder.append("\nif count and tonumber(count) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then");
luaBuilder.append("\nreturn count;");
luaBuilder.append("\nend");
//执行计算器自增
luaBuilder.append("\ncount = redis.call('incr',KEYS[1])");
//从第一次调用开始限流
luaBuilder.append("\nif tonumber(count) == 1 then");
//设置过期时间
luaBuilder.append("\nredis.call('expire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2])");
luaBuilder.append("\nend");
luaBuilder.append("\nreturn count;");
return luaBuilder.toString();
}
}
2.4限流切面实现
/**
* 描述:限流切面实现
*
* @author 程序员小强
**/
@Aspect
@Configuration
public class RateLimitAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RateLimitAspect.class);
private RedisRateLimitComponent redisRateLimitComponent;
@Autowired
public RateLimitAspect(RedisRateLimitComponent redisRateLimitComponent) {
this.redisRateLimitComponent = redisRateLimitComponent;
}
/**
* 匹配所有使用以下注解的方法
*
* @see RateLimit
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.ratelimit.annotation.RateLimit)")
public void pointCut() {
}
@Around("pointCut()&&@annotation(rateLimit)")
public Object logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RateLimit rateLimit) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
String methodName = signature.getMethod().getName();
//组装限流key
String rateLimitKey = this.getRateLimitKey(joinPoint, rateLimit);
//限流组件-通过计数方式限流
Long count = redisRateLimitComponent.rateLimit(rateLimitKey, rateLimit.time(), rateLimit.count());
logger.debug("[ RateLimit ] method={},rateLimitKey={},count={}", methodName, rateLimitKey, count);
if (null != count && count.intValue() <= rateLimit.count()) {
//未超过限流次数-执行业务方法
return joinPoint.proceed();
} else {
//超过限流次数
logger.info("[ RateLimit ] >> over the max request times method={},rateLimitKey={},currentCount={},rateLimitCount={}",
methodName, rateLimitKey, count, rateLimit.count());
throw new RateLimitException(rateLimit.msg());
}
}
/**
* 获取限流key
* 默认取 RateLimit > key 属性值
* 若设置了 keyField 则从参数中获取该字段的值拼接到key中
* 示例:user_phone_login_max_times:13235777777
*
* @param joinPoint
* @param rateLimit
*/
private String getRateLimitKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RateLimit rateLimit) {
String fieldName = rateLimit.keyField();
if ("".equals(fieldName)) {
return rateLimit.key();
}
//处理自定义-参数名-动态属性key
StringBuilder rateLimitKeyBuilder = new StringBuilder(rateLimit.key());
for (Object obj : joinPoint.getArgs()) {
if (null == obj) {
continue;
}
//过滤基本类型参数
if (ReflectionUtil.isBaseType(obj.getClass())) {
continue;
}
//属性值
Object fieldValue = ReflectionUtil.getFieldByClazz(fieldName, obj);
if (null != fieldValue) {
rateLimitKeyBuilder.append(":").append(fieldValue.toString());
break;
}
}
return rateLimitKeyBuilder.toString();
}
}
由于演示项目中做了统一异常处理
在限流切面这里未做异常捕获,若超过最大限流次数会抛出自定义限流异常。可以根据业务自行处理。
/**
* 反射工具
*
* @author 程序员小强
*/
public class ReflectionUtil {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReflectionUtil.class);
/**
* 根据属性名获取属性元素,
* 包括各种安全范围和所有父类
*
* @param fieldName
* @param object
* @return
*/
public static Object getFieldByClazz(String fieldName, Object object) {
Field field = null;
Class<?> clazz = object.getClass();
try {
for (; clazz != Object.class; clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()) {
try {
//子类中查询不到属性-继续向父类查
field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException ignored) {
}
}
if (null == field) {
return null;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(object);
} catch (Exception e) {
//通过反射获取 属性值失败
logger.error("[ ReflectionUtil ] >> [getFieldByClazz] fieldName:{} ", fieldName, e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 判断对象属性是否是基本数据类型,包括是否包括string | BigDecimal
*
* @param clazz
* @return
*/
public static boolean isBaseType(Class clazz) {
if (null == clazz) {
return false;
}
//基本类型
if (clazz.isPrimitive()) {
return true;
}
//String
if (clazz.equals(String.class)) {
return true;
}
//Integer
if (clazz.equals(Integer.class)) {
return true;
}
//Boolean
if (clazz.equals(Boolean.class)) {
return true;
}
//BigDecimal
if (clazz.equals(BigDecimal.class)) {
return true;
}
//Byte
if (clazz.equals(Byte.class)) {
return true;
}
//Long
if (clazz.equals(Long.class)) {
return true;
}
//Double
if (clazz.equals(Double.class)) {
return true;
}
//Float
if (clazz.equals(Float.class)) {
return true;
}
//Character
if (clazz.equals(Character.class)) {
return true;
}
//Short
return clazz.equals(Short.class);
}
}
3.测试一下
基本属性已经配置好了,写个接口测试一下。
3.1方法限流示例
/**
* 计数器
* 演示 demo 为了方便计数
*/
private static final AtomicInteger COUNTER = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* 普通限流
* <p>
* 30 秒中,可以访问10次
*/
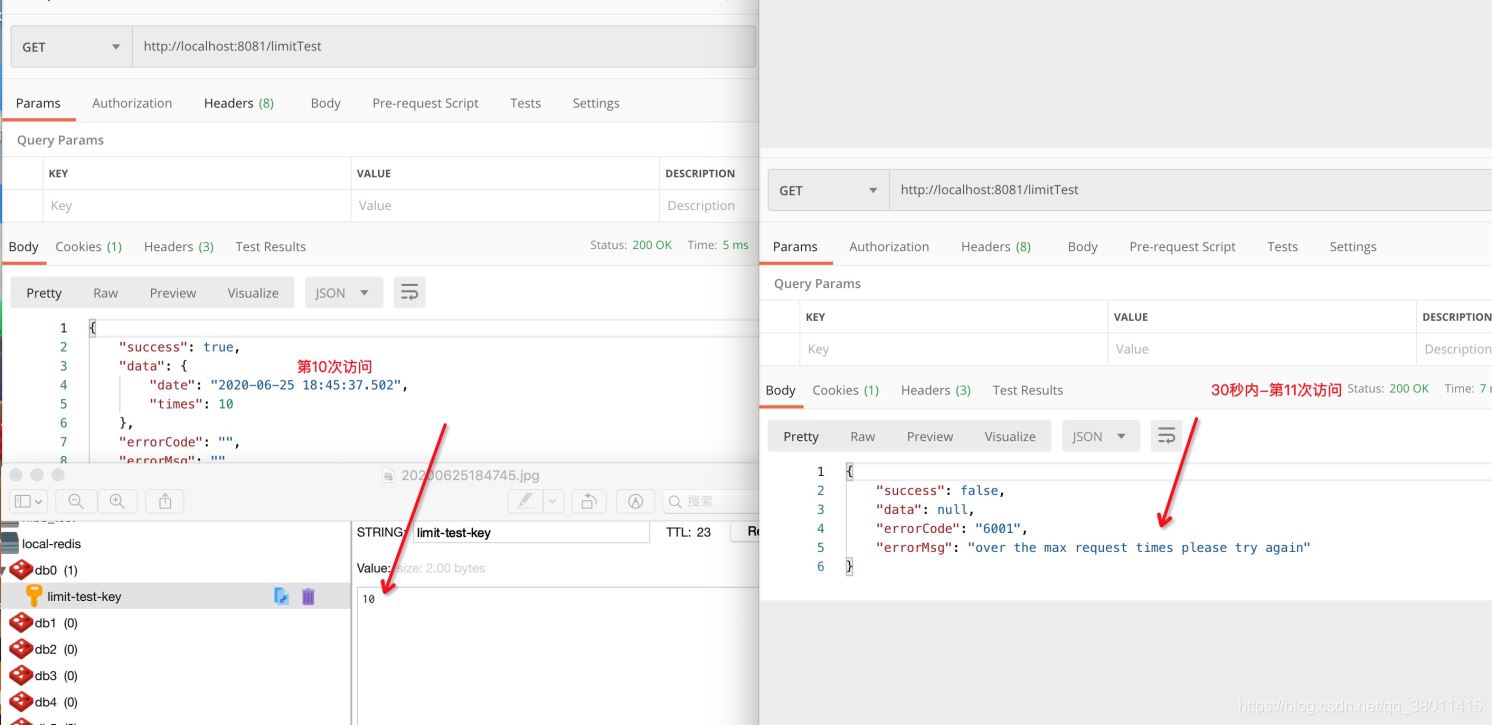
@RequestMapping("/limitTest")
@RateLimit(key = "limit-test-key", time = 30, count = 10)
public Response limitTest() {
Map<String, Object> dataMap = new HashMap<>();
dataMap.put("date", DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"));
dataMap.put("times", COUNTER.incrementAndGet());
return Response.success(dataMap);
}
3.2动态入参限流示例
3.2.1场景一:5分钟内,方法最多访问10次,根据入参手机号限流
入参类
public class UserPhoneCaptchaRateParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1L;
private String phone;
//省略 get/set
}
private static final Map<String, AtomicInteger> COUNT_PHONE_MAP = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 根据手机号限流-限制验证码发送次数
* <p>
* 示例:5分钟内,验证码最多发送10次
*/
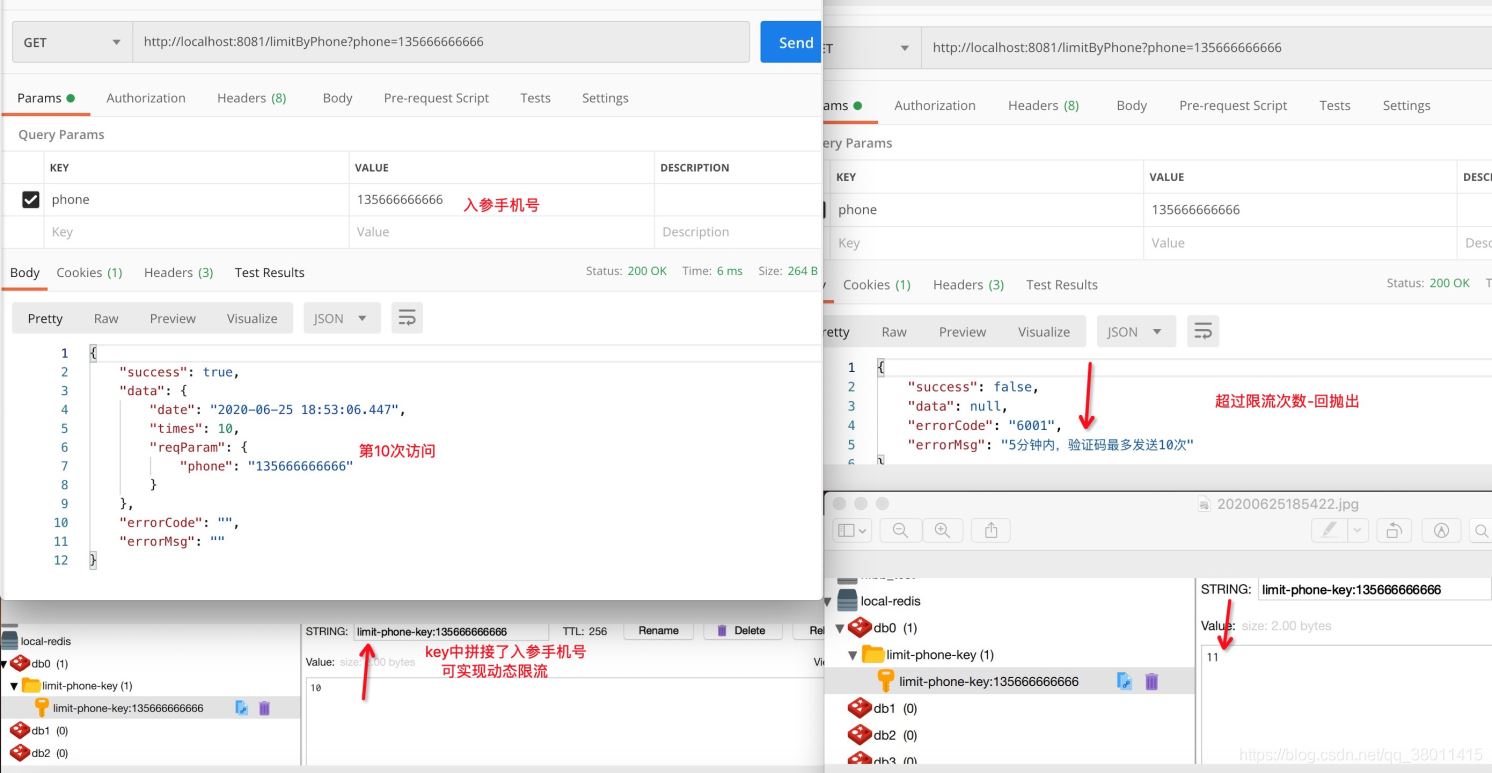
@RequestMapping("/limitByPhone")
@RateLimit(key = "limit-phone-key", time = 300, count = 10, keyField = "phone", msg = "5分钟内,验证码最多发送10次")
public Response limitByPhone(UserPhoneCaptchaRateParam param) {
Map<String, Object> dataMap = new HashMap<>();
dataMap.put("date", DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"));
if (COUNT_PHONE_MAP.containsKey(param.getPhone())) {
COUNT_PHONE_MAP.get(param.getPhone()).incrementAndGet();
} else {
COUNT_PHONE_MAP.put(param.getPhone(), new AtomicInteger(1));
}
dataMap.put("times", COUNT_PHONE_MAP.get(param.getPhone()).intValue());
dataMap.put("reqParam", param);
return Response.success(dataMap);
}
3.2.2场景二:根据订单ID限流
入参类
@Data
public class OrderRateParam implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1L;
private String orderId;
//省略 get\set
}
private static final Map<String, AtomicInteger> COUNT_ORDER_MAP = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 根据订单ID限流示例
* <p>
* 300 秒中,可以访问10次
*/
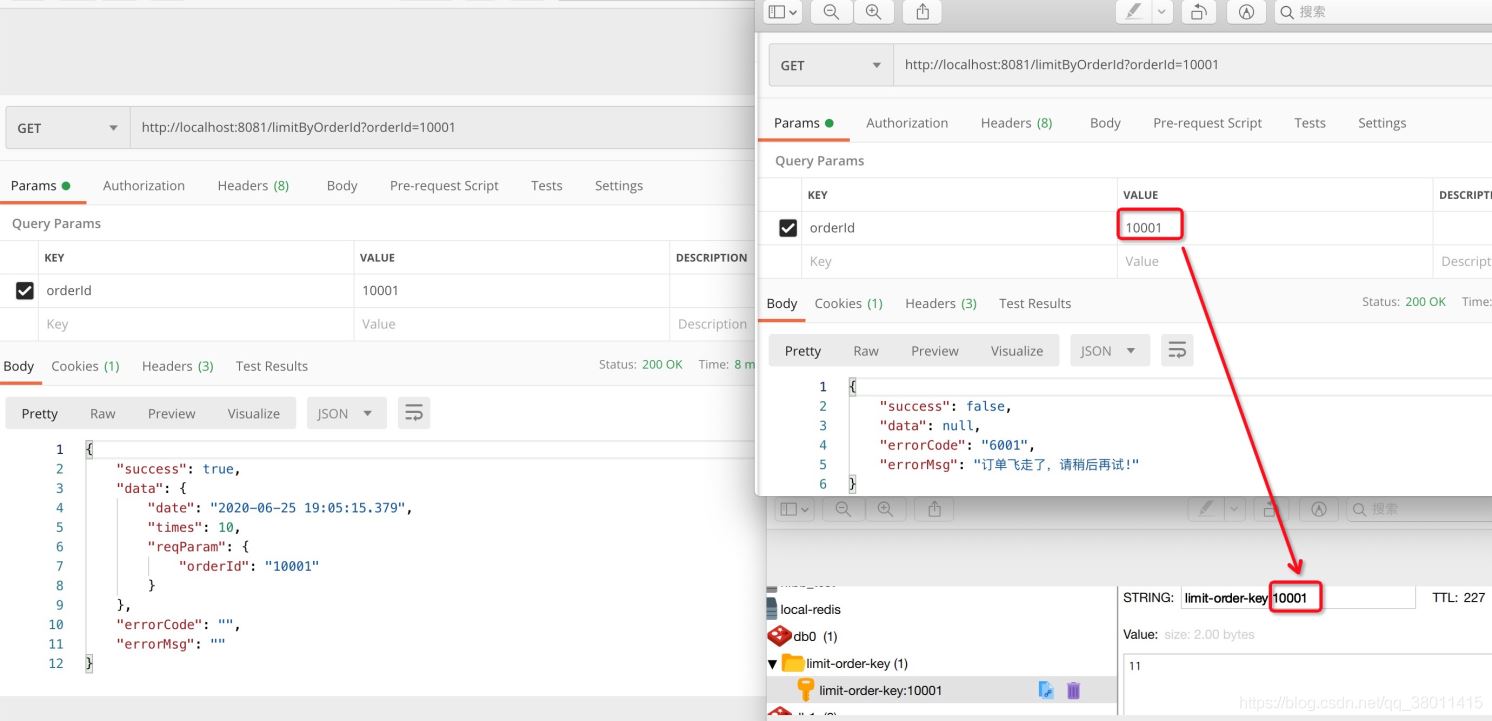
@RequestMapping("/limitByOrderId")
@RateLimit(key = "limit-order-key", time = 300, count = 10, keyField = "orderId", msg = "订单飞走了,请稍后再试!")
public Response limitByOrderId(OrderRateParam param) {
Map<String, Object> dataMap = new HashMap<>();
dataMap.put("date", DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"));
if (COUNT_ORDER_MAP.containsKey(param.getOrderId())) {
COUNT_ORDER_MAP.get(param.getOrderId()).incrementAndGet();
} else {
COUNT_ORDER_MAP.put(param.getOrderId(), new AtomicInteger(1));
}
dataMap.put("times", COUNT_ORDER_MAP.get(param.getOrderId()).intValue());
dataMap.put("reqParam", param);
return Response.success(dataMap);
}
4.其它扩展
根据ip限流
在key中拼接IP即可;
5.源码地址
到此这篇关于Redis分布式限流组件设计与使用实例的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Redis分布式限流内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!

